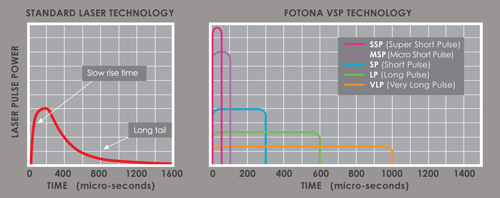
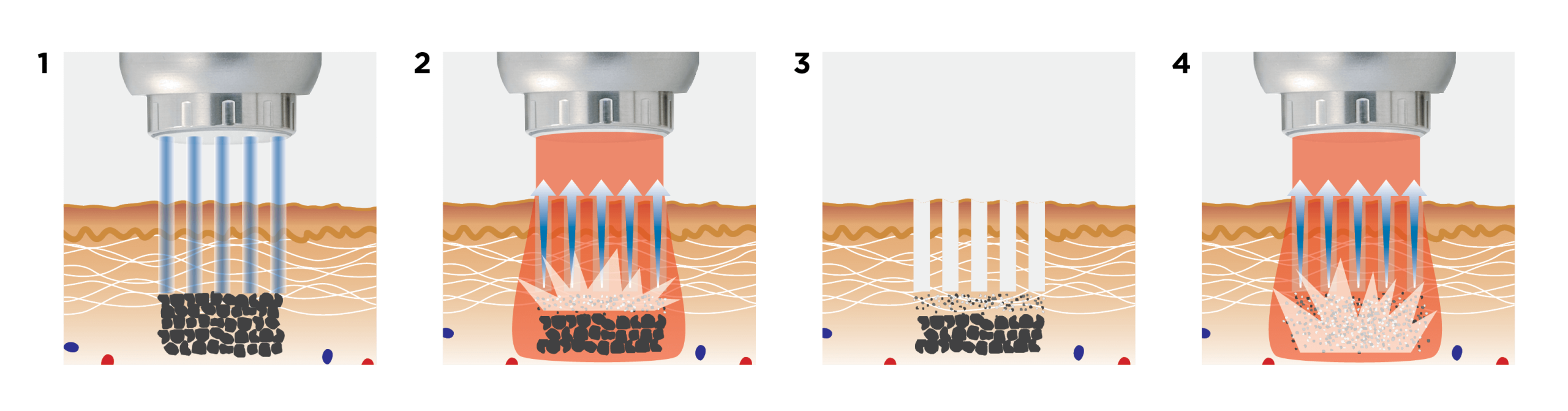
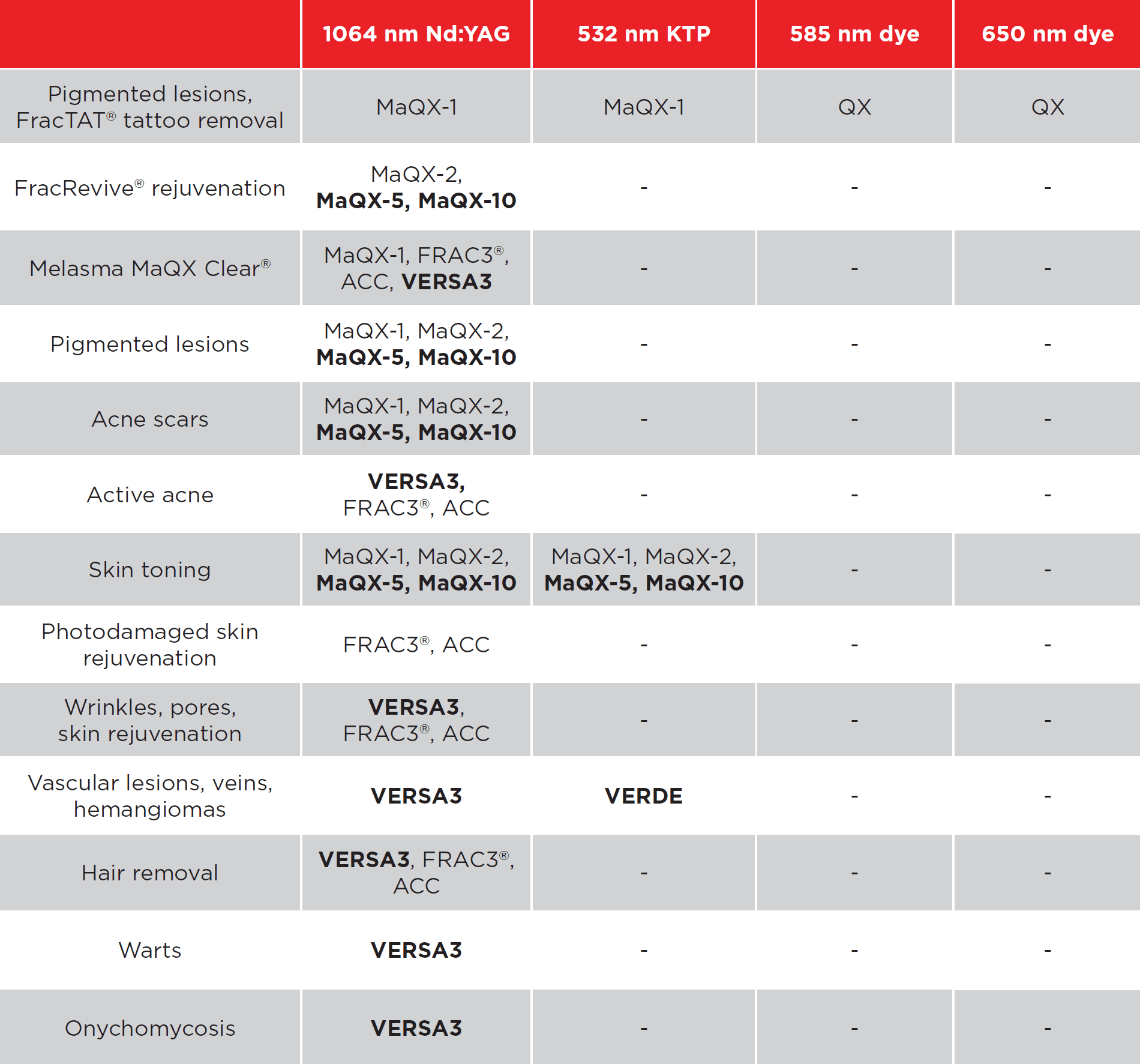
When you begin researching lasers you may notice that two wavelengths stand out for their versatility and broad range of applications. Nd:YAG and Er:YAG lasers are some of the most advanced available on the market, they can treat aesthetic and medical conditions, making them a great choice for business owners and clinicians. These two wavelengths are integral to many of Fotona’s most popular treatments and devices. Fotona’s development of Er:YAG and Nd:YAG lasers have improved the functioning and modality of these technologies to create powerful treatment solutions that have revolutionised the medical aesthetics market. Here we will explore what Nd:YAG and Er:YAG lasers are and how they work, we also explain why Fotona’s Er:YAG and Nd:YAG modalities are different to every other laser on the market.
Understanding Laser Technology
The Basics of Laser Technology
Laser technology is best understood by looking at the fundamentals of light energy and physics. In fact, the word laser stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. If we look at the spectrum of light we can see that this spans from invisible light to visible light. Both Nd:YAG and Er:YAG are classified as infrared light although the length of the wavelength differs which alters their function. By precisely controlling the emission of light through a device you can use laser technology for various medical and aesthetic applications. There are several key properties of laser light including the following:
- Monochromatic: This means that the light emitted is a single wavelength.
- Coherent: Laser light waves move in unison, which means that they are in phase.
- Collimated: The light is directed in a narrowly focused beam. In fractional lasers, the light is still collimated but the beam is fractionated by the handpiece creating multiple beams of light.
These properties provide the basis for how lasers can be used, depending on the treatment and laser you can target specific tissues and minimise damage to surrounding tissues. One of the benefits of Fotona Lasers in particular is that they have adapted and developed laser technology to optimise the precision of the treatments, reducing risk and downtime whilst optimising results.
What is an Nd:YAG Laser?
Definition and Characteristics
Nd:YAG laser operates at a wavelength of 1064 nanometers and its light fits within the infrared classification of light. It’s classified as a solid-state laser, which means that in order for the Nd:YAG laser to function it must work in the following way. Inside the laser, there is an Nd:YAG rod which is made up of a yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG) crystal in which some of the ions have been replaced with neodymium ions. The crystal itself serves no function other than to host the neodymium ions. In addition to the crystal, there is a krypton arc lamp which is powered by the device. These two entities are contained in an elliptical reflector to ensure no light energy is wasted and the light emitted from the lamp is reflected onto the rod. When the lamp is on it excites the neodymium ions to their highest level, the energy then drops through a process called spontaneous emission and stabilises at the metastable state of 1064 nanometres which can be emitted in the form of a laser beam.
Nd:YAG stands for Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet, it’s known for its deep penetration into the skin. This makes it suitable for treating deeper tissues and the chromospheres (light absorbing molecules) that sit there.
How Nd:YAG Lasers Work?
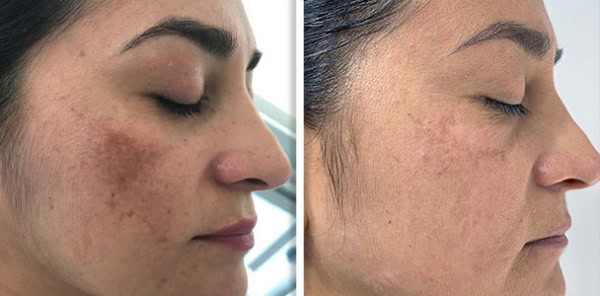
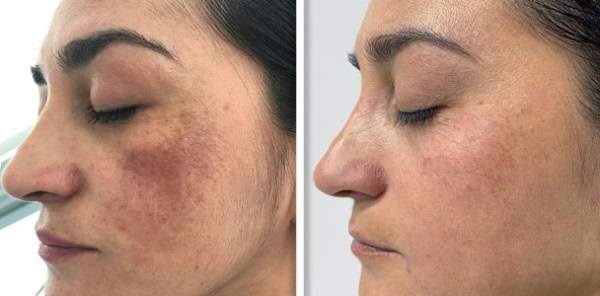
The laser light emitted from an Nd:YAG laser is absorbed into specific chromophores in the skin, namely melanin and haemoglobin. The light waves are converted into heat which then targets the chromophore where it is absorbed, this can be used to treat conditions such as pigmentation, vascular lesions and hair follicles to name a few. The heat energy then destroys its target, if you take pigment as an example, the Nd:YAG laser destroys the melanin causing the pigmentation. Because the laser is targeted and only absorbed into specific chromophores it doesn’t damage surrounding healthy tissue, making it a safe popular treatment modality.
Applications of Nd:YAG Lasers
With its deep absorbency and precision, Nd:YAG lasers are very versatile and can be used for numerous medical and aesthetic treatments, including:
Hair Removal: Nd:YAG laser hair removal can be a highly effective method of hair removal and can safely be used in all skin types, good news of for those with darker skin types who are unable to access many forms of hair removal due to the risk of skin damage, burning and hyperpigmentation. This treatment works because the Nd:YAG laser wavelength is absorbed by the melanin in the hair follicles, which damages the hair follicle at its root and prevents future hair growth.
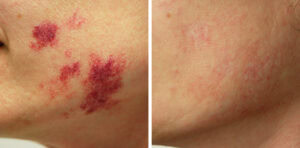
Vascular Lesions: Nd:YAG lasers can be used effectively to treat vascular lesions such as spider veins, haemangiomas and blood vessels. The Nd:YAG laser is absorbed into the haemoglobin which coagulates the blood vessels that connect to the target vascular lesions, causing the target vessel to collapse. The precision of a Fotona vascular treatment ensures no other vascular networks are affected.
Skin Rejuvenation: Nd:YAG lasers can be used for skin rejuvenation treatments, the deep penetration of the laser can stimulate collagen production, which results in firmer more youthful-looking skin.
Tattoo Removal: Nd:YAG lasers can be used in Q-switched mode to successfully treat and remove tattoos. This is particularly successful in darker ink colours as the laser breaks down the ink particles.
What is an Er:YAG Laser?
Definition and Characteristics
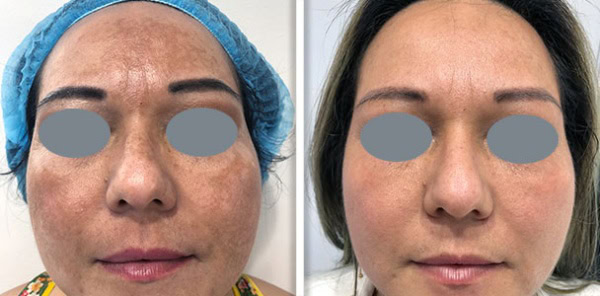
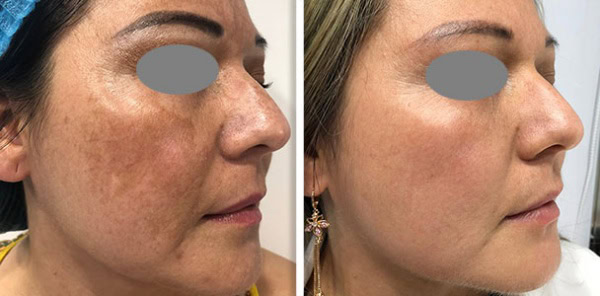
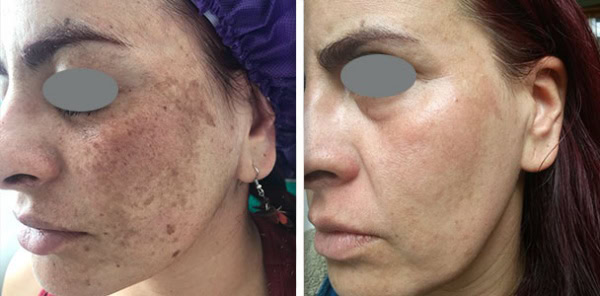
Er:YAG stands for Erbium-doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet, it is also a solid-state laser but it operates at a laser wavelength of 2940nm. The Er:YAG laser wavelength is absorbed in water and, therefore, penetrates much more superficially than Nd:YAG this makes it ideal for ablative treatments that target the skin surface, such as benign lesion removal and fractional resurfacing.
Fotona has further developed Er:YAG technology to produce its unique SMOOTH mode. This mode works by emitting rapid short pulses of Er:YAG laser to heat the tissues without damaging the epidermal layers. The heat triggers the fibroblasts and the production and restructuring of collagen fibres. This modality has many different applications, including facial rejuvenation, snoring and gynaecology.
How Er:YAG Lasers Work?
The laser emits a high-intensity beam of light that is absorbed in the water of the skin’s tissue. As the water heats up it causes the water to vaporise and destroys the tissues surrounding it due to the thermal effect. Er:YAG can also be used in a precise manner to effectively remove tissue such as benign skin lesions.
Alternatively in Fotona SMOOTH mode, the gentle heating of the tissues stimulates the production of collagen without damaging any tissues, so you can see the true versatility of this laser.
Applications of Er:YAG Lasers?
Er:YAG lasers are some of the most versatile and they can be used across the domains of aesthetics, gynaecology, medicine and dentistry. Some of these applications include:
Skin Resurfacing
Er:YAG are renowned for setting the gold standard for skin resurfacing procedures. They work by removing the top layers of damage and encouraging the growth and repair of healthy skin. This treatment is used to improve the texture of the skin and the appearance of scars and wrinkles. Fotona’s Erbium has a patented square pulse technology which means there is no collateral damage to the skin not being targeted during the procedure, this minimises any risk of collateral damage and optimises healing and results.
Acne Scars
Acne scars don’t stand a chance against the power of an Er:YAG laser. Depending on the type of scar, there is a different approach to treatment. However in general this treatment works by removing damaged skin and stimulating collagen production. The result is smoother skin with improved texture and tone, giving renewed confidence to those treated.
Fractional Resurfacing
Fractional resurfacing has gained in popularity over the years and for good reason, by creating micro-injuries and micro-columns of skin, you can trigger the body’s healing response. This helps to produce collagen and works to improve several different skin concerns, including texture, ageing skin and scarring. Due to the precision of the fractional beam recovery is quite and results outstanding.
Wart and Lesion Removal
Although the thorough treatment of a wart often involves using a combined approach of Er:YAG and Nd:YAG. Er:YAG can be extremely useful to remove the build-up of dead skin and ablating dead tissue. The precision of an Er:YAG laser is a perfect choice for the removal of benign lesions such as moles etc. Whilst Nd:YAG is our go to for warts as it also kills off the viral cause.
Combining Nd:YAG and Er:YAG Lasers: Fotona’s TwinLight Technology
The Power of Dual-Wavelength Lasers
In both the SP Dynamis line and the StarWalker, you have the benefit of both Er:YAG and Nd:YAG lasers within one system. This is hugely advantageous for many reasons and allows practitioners to offer a comprehensive range of treatments whilst optimising on space and efficiency.
This versatility of the TwinLight technology not only allows you to broaden treatment offerings, it also improves the effectiveness of treatments allowing you to target different layers of tissue to enhance results.
If you would like to learn more about the power of a Fotona device, the types of treatments that you can provide and the benefits of a TwinLight system, contact us today via email at: info@fotonauk.co.uk, call us on 0118 370 9314, or even WhatsApp us on 07376 309178. We look forward to welcoming you into the wonderful Fotona Family.